Unveiling Dental Attrition: Causes, Prevention, and Treatment
What is Dental Attrition?
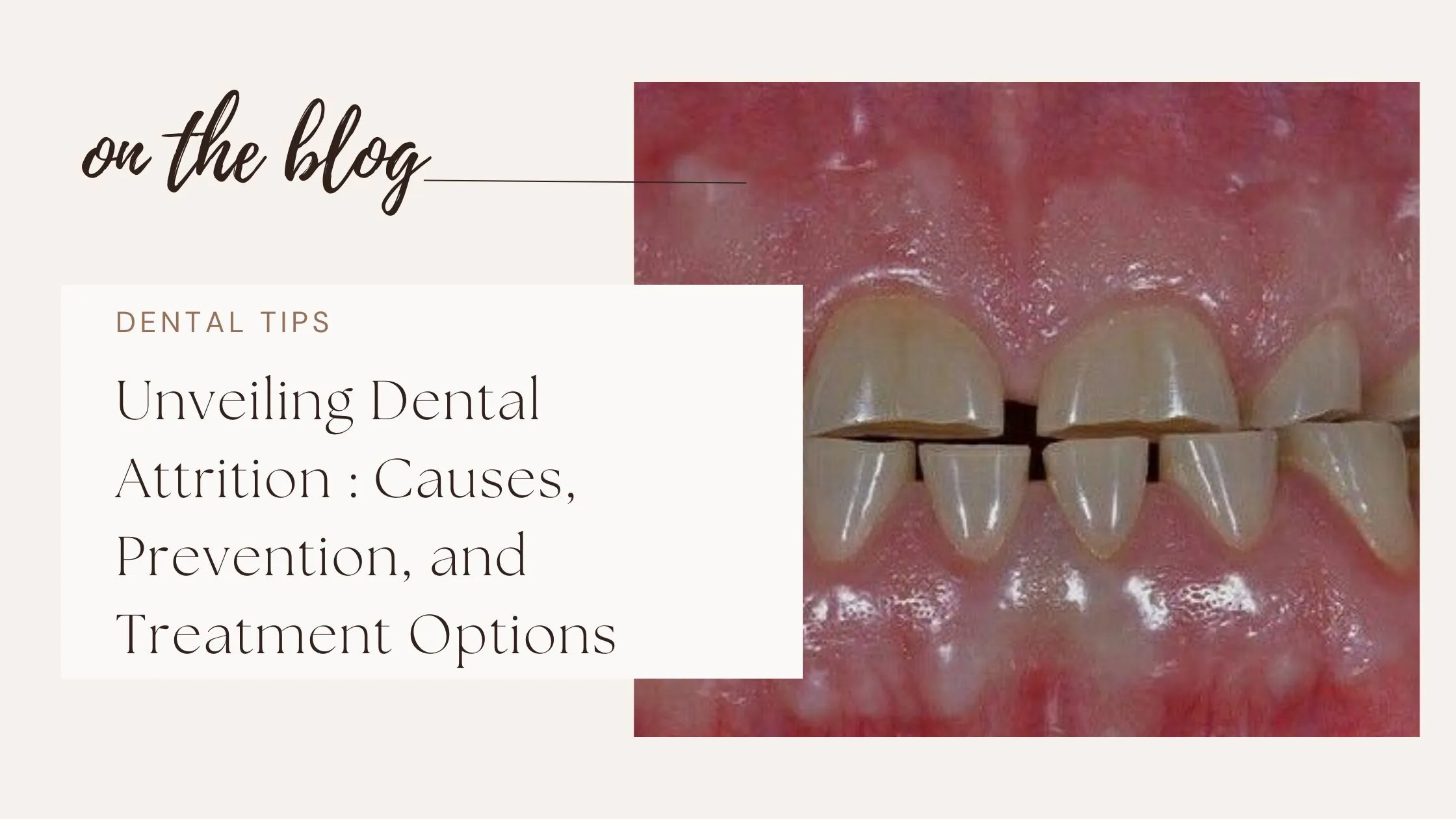
Dental attrition is the gradual loss of tooth structure resulting from constant tooth grinding.
This chronic friction between opposing teeth causes mechanical wear of tooth enamel and dentin in a few cases.
Attrition is usually noticed on incisal or occlusal surfaces of teeth (biting surfaces), giving the teeth a flattened appearance.
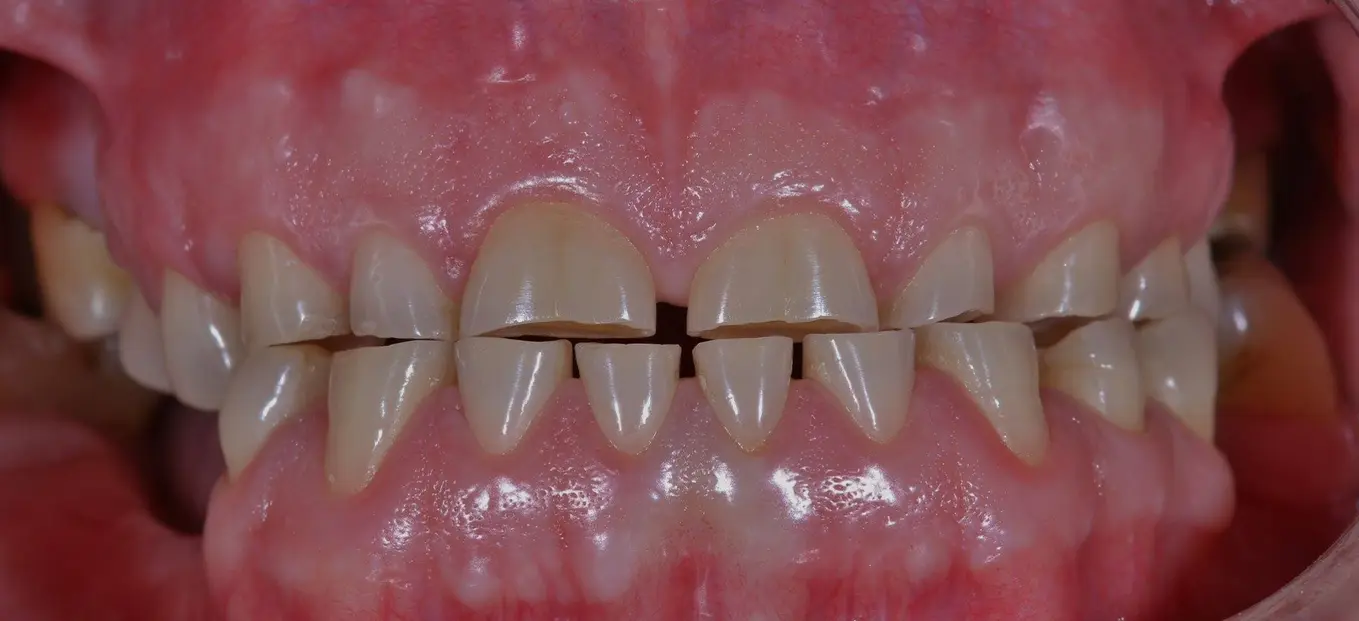
Types of Tooth Wear
Dental attrition is a kind of tooth wear; other types of tooth wear include.
Dental Abrasion
- Dental abrasion is the wearing away of tooth substance through an abnormal mechanical process.
- It usually occurs as a result of external forces acting on teeth.
- Abrasion is usually noticed along the cervical margins of the teeth (near the gum line).
- A few causes for dental abrasion include vigorous tooth brushing techniques, use of abrasive toothpastes, use of hard-bristled toothbrushes, etc.
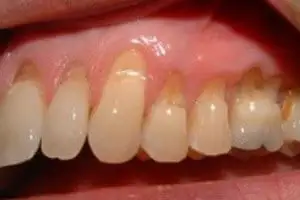
Dental Erosion
- Dental erosion is an irreversible loss of tooth structure by a chemical process without the involvement of bacteria.
- The loss of tooth structure occurs as a result of contact with acids introduced in the oral cavity from intrinsic sources such as frequent vomiting, gastroesophageal reflux, etc., or from extrinsic sources like frequent consumption of carbonated drinks, drugs like chewable vitamin C tablets, acidic foods, and fruits, etc.
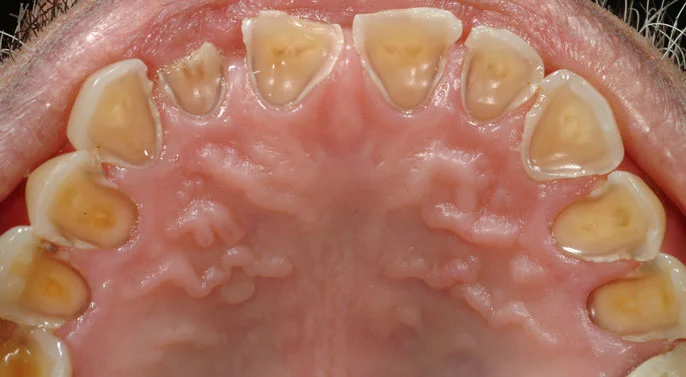
Abfraction
- Abfraction is the loss of tooth structure usually found near the gingival margins (gum line).
- This is not a cavity but a result of abnormal forces acting on teeth during biting, eating, grinding, etc. Such repetitive stress causes enamel loss at cervical areas.
- They are clinically seen as wedge-shaped notches near the gum line.
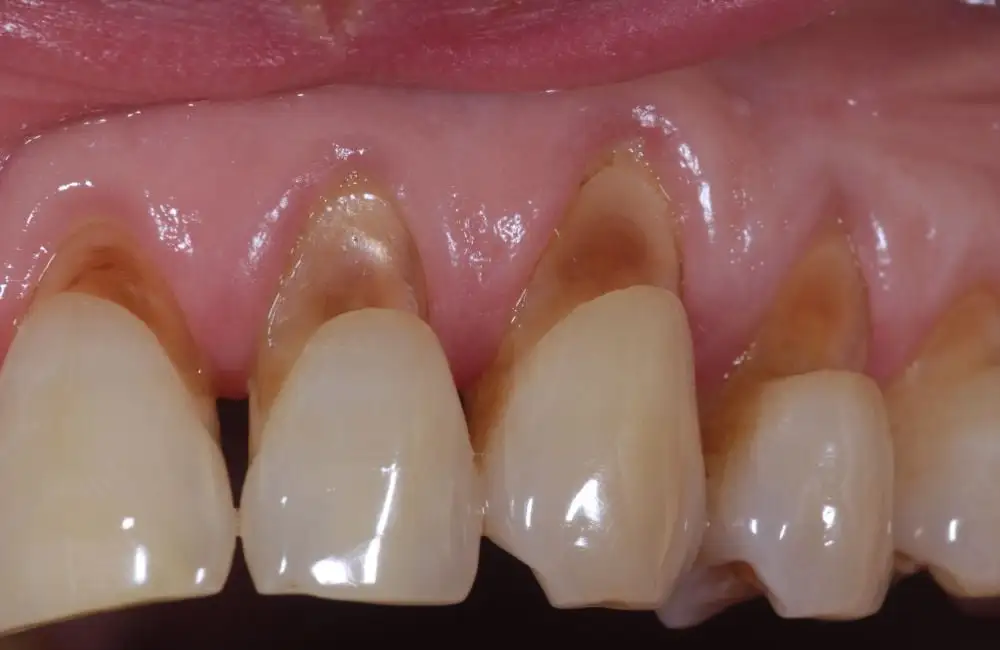
Causes of Dental Attrition
Dental attrition occurs due to continuous mechanical wear on teeth caused by various factors. Understanding these causes can help in early prevention and management. Below are the most common reasons for dental attrition:
- Bruxism
- Grinding or clenching of teeth causes dental attrition as a result of constant mechanical forces being applied to the teeth.
- Teeth are subjected to intense pressure and friction, which causes gradual wearing down of tooth structure.
- Bruxism also contributes to other problems like temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders causing jaw pain, clicking sounds, etc.
- Aging
- Dental attrition is a natural part of aging because of continuous wear and tear of teeth as they are subjected to chewing, grinding, and biting forces for years.
- Malaligned teeth
- Improper position of teeth causes unequal stress distribution, leading to abnormal contact points and uneven repetitive wear and tear of teeth in certain areas.
- Dietary Habits
- Diets containing hard or abrasive foods like nuts, hard candies, etc., often require increased force for mastication, leading to an increased mechanical stress on teeth, which causes dental attrition.
- Acidic foods also cause erosion of teeth, which weakens the enamel and increases the susceptibility for attrition of teeth.
Signs & Symptoms of Dental Attrition
Dental attrition gradually affects the structure and appearance of teeth, leading to noticeable changes over time. Early detection of these signs can help prevent further damage and maintain oral health. Below are the key symptoms to look out for:
Increased Tooth Sensitivity
- Dental attrition causes wearing down of the enamel layer, thereby exposing the underlying dentin.
- Consumption of hot or cold foods and drinks results in hypersensitivity leading to pain and discomfort.
Flattened or Shortened Teeth
- Continuous tooth-to-tooth contact causes loss of enamel over a period of time, which results in loss of particular tooth characteristics and also gives the teeth an uneven, flattened appearance.
- This loss of tooth contours reduces the aesthetic appeal of teeth.
Enamel Thinning
- Enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body. Continuous grinding and biting forces on teeth over the years result in thinning of the enamel layer, which makes the tooth susceptible to sensitivity, esthetic concerns, and tooth decay.
Jaw Pain
- Jaw pain results from continuous clenching of teeth and causes frequent headaches and jaw pains because of the strain on the muscles of the jaw.
Changes in Bite and Occlusion
- Dental attrition causes loss of tooth structure, which alters the bite and affects the jaw position and aesthetics.
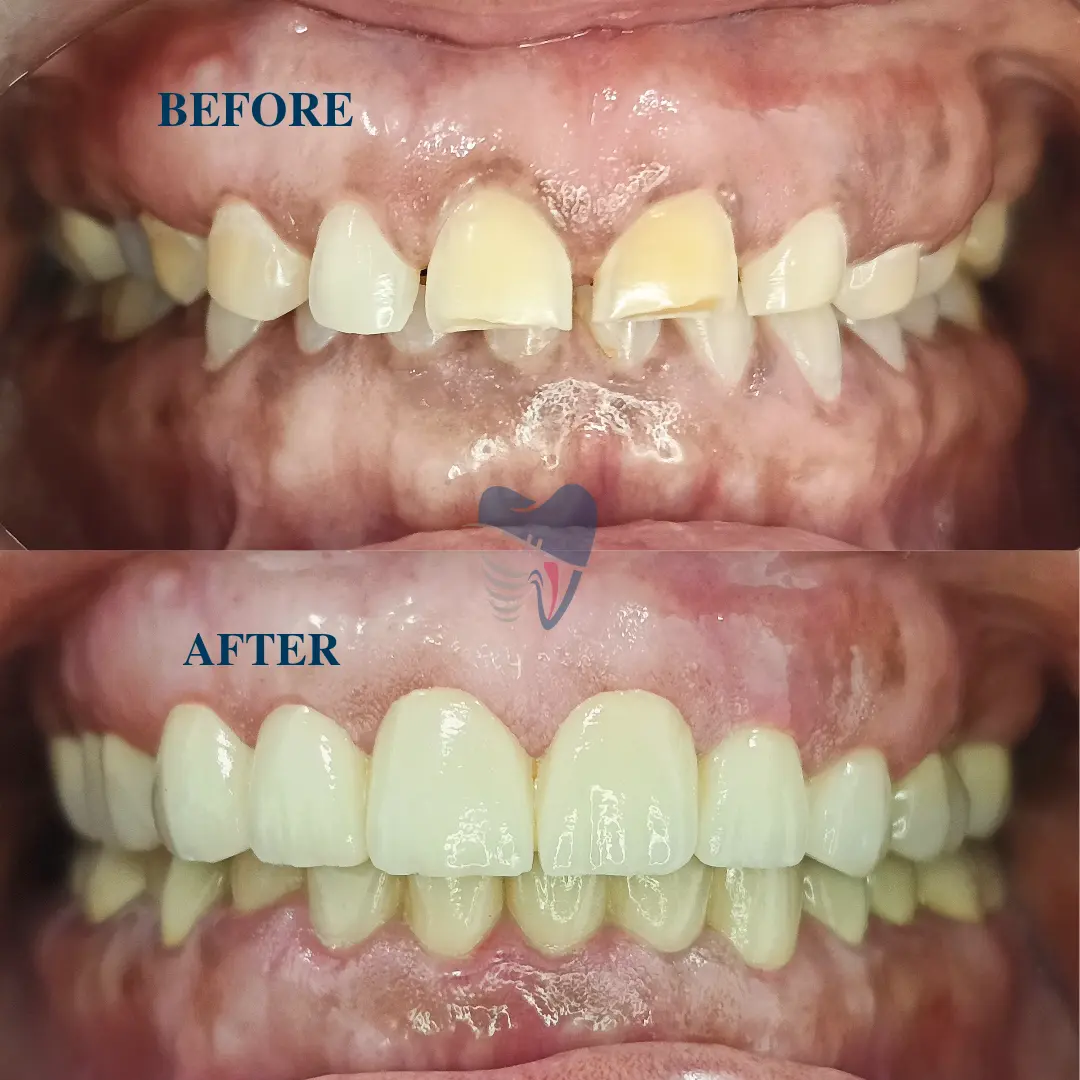
Best Treatment Options for Dental Attrition
The treatment for dental attrition depends on the severity of tooth wear and its underlying cause. Early intervention can help protect teeth from further damage and restore their function and appearance. Below are the most effective treatment options:
Night Guards & Splints
- If the cause of dental attrition is bruxism, then a custom-made night guard would protect the teeth by providing a barrier between the upper and lower teeth.
Orthodontic Treatment
- If dental attrition is caused because of mal-aligned teeth, orthodontic treatment like braces or aligners helps to correct the alignment of teeth and facilitate correct positioning of teeth. This helps in correcting the bite, thereby reducing the stress on certain areas of teeth and preventing further wear.
Restorative Dental Treatments
- For teeth that are affected by mild to moderate attrition, dental bonding can be done to restore the lost tooth structure and esthetics. This procedure is done by applying a tooth-colored resin material, and the shaping and polishing of the filling is done to provide a natural tooth shape.
- For teeth that are severely affected by attrition, crowns or veneers may be required to restore the function and esthetics. These cover the teeth entirely or partially and protect them from further damage and restore the esthetics.
Full Mouth Rehabilitation (FMR)
- In advanced cases, Full Mouth Rehabilitation (FMR) treatment is considered to restore severely attrited teeth. Such cases exhibit severe bite collapse, affecting proper functioning like chewing difficulty and speech impairment because of significant loss of tooth structure.
- Fluoride treatments and dental sealants also provide a protective layer on teeth for minor attrition.
Dietary Adjustments
- Reducing hard, chewy, or abrasive foods helps to reduce the forces exerted on teeth and prevent progressive wear of teeth.
- Limiting acidic foods and beverages helps to reduce weakening of enamel and reduce the susceptibility of attrition.
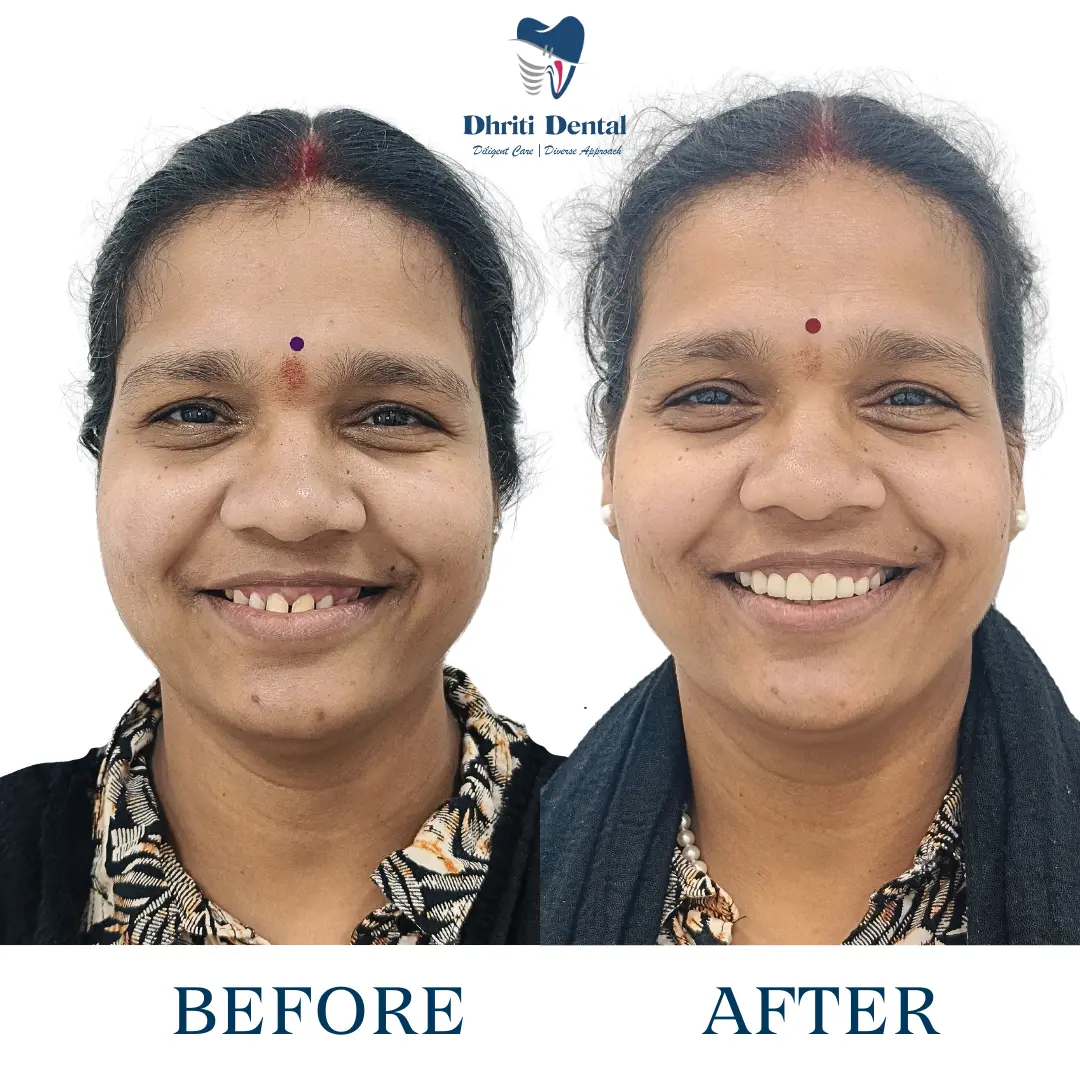

Prevention Tips for Dental Attrition
- Practicing good oral hygiene and regular brushing with fluoride toothpaste with appropriate brushing techniques and using a soft-bristled toothbrush can help to maintain the health of teeth and surrounding tissues.
- Avoid habits like nail biting and clenching by using techniques that help to relieve stress.
- Wearing a night guard to protect the teeth from continuous friction.
- Routine dental checkups may help to detect attrition earlier.
If you're looking for the best treatment for dental attrition, visit Dhriti Dental, the best dental clinic in Hyderabad. Our expert team provides advanced care to restore and protect your teeth for a healthy, confident smile.
FAQs About Dental Attrition
1. Can dental attrition lead to serious problems?
Yes, dental attrition can cause serious problems with teeth if left untreated. It causes sensitivity and pain and leaves the teeth at risk for infections and fractures because of the weakened structure of the tooth. It can also cause misalignment of teeth, TMJ disorders, and difficulty chewing. Early intervention helps to prevent such problems.
2. Can dental attrition be reversed?
No, dental attrition cannot be reversed. But further attrition can be prevented by early intervention with restorative treatments, occlusal protection by using a night guard, etc.
3. Should I see a dentist if I have a mild attrition?
Yes, consulting a dentist in case of mild attrition will help to identify the cause and provide suitable treatment to prevent progression of attrition.