
Tobacco and it’s products have been used for centuries, with their origins tracing back to South America where it was used by the indigenous people for both cultural and medicinal purposes. With time it’s use has spread across civilizations, currently it is used by over 22% of the world’s population.
Although many studies and have outlined the harmful effects of it’s use there is a continued rise in its usage especially in developing countries like India. Smoking is one of the most common ways of using tobacco.
Smoking can cause multiple systemic and oral health problems, these include cancer, decreased immunity, ulcers etc.
The major reason for its persistent use is nicotine, which stimulates specific centers in the brain, releasing dopamine which creates a sense of reward and pleasure.
However, despite its addictive nature, quitting tobacco is possible with the right support and strategies. This blog outlines the potential hazards associated with tobacco usage and the beneficial effects on its cessation.

Tobacco is ranked the 3rd most addictive and 7th most harmful of 20 commonly used drugs. There are about 80 carcinogens ( Cancer causing agents) in a cigarette.
Nicotine although does not have a direct effect on the body but it aids in the process and is considered a cocarcinogen. Smoking a cigarette is associated with the risk of 12 types of cancers, apart from this there is also risk of developing cardiac and respiratory disorders.
Nicotine although does not have a direct effect on the body but it aids in the process and is considered a cocarcinogen. Smoking a cigarette is associated with the risk of 12 types of cancers, apart from this there is also risk of developing cardiac and respiratory disorders.
Some of the effects of smoking on our body are listed below

The chain smoker: He does not devour it, it devours him
Smoking can have many effects on oral health with some of them are discussed below:
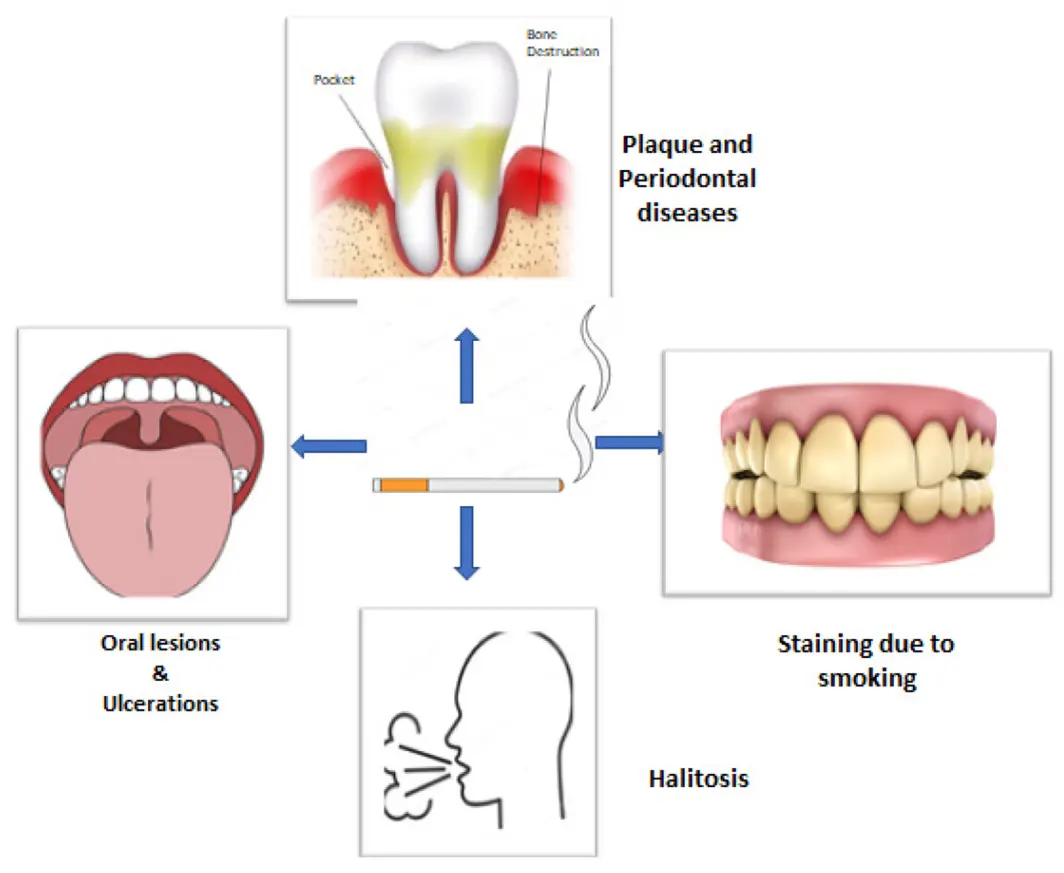
The cancer of the oral cavity and the voice box are the most common effects of long-term smoking after lung cancer. Oral cancers include cancers of the tongue, cheek or lips.
The risk of oral cancer is approximately 3.43 times higher in smokers when compared to non-smokers. Smoking along with alcohol abuse can further increase the risk of oral cancer.
Smoking exerts a strong untoward effect on periodontal health, it makes the immune system weaker, making it more prone to harmful bacteria causing gum diseases- periodontitis. The progression of the disease is also faster among the smokers, which can ultimately lead to tooth loss.
Impact of smoking -
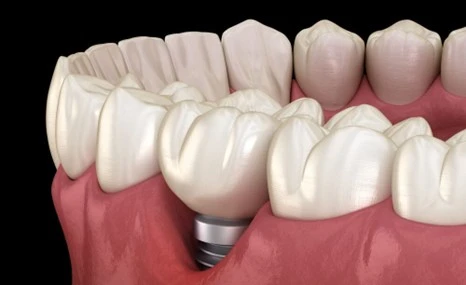
There is a higher risk of implant failure among smokers compared to non-smokers primarily due to periimplantitis and progressive bone loss. This is associated with bleeding around implants, loss of gums around implants, loose implants, pain and ultimately loss of the implant.
Smokers also carry a increased risk of developing caries as the cigarette smokes impairs salivary function, which has an important protective role against dental caries.
It also affects the buffering capacity of saliva which may also affect susceptibility to caries.
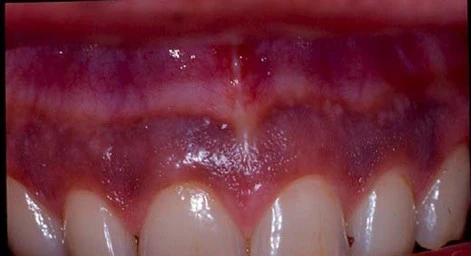
Smoking cessation has significant benefits
Smoking continues to be a significant risk to oral health. There are multiple oral diseases linked with smoking. Smoking cessation not only improves the oral and systemic health, but, also improves the quality of life of a person.
There are multiple ways one can try to give up the deleterious habit of smoking, all it takes is the will and correct guidance.
Let’s take a step toward a tobacco free future one breath a time.
Want to give up smoking or get screened for oral cancer? Book an appointment with our Oral and Maxillofacial Oncosurgeon at Dhriti Dental, Nallagandla or at Manikonda, Hyderabad. Our team provides personalised plans to help you give up your smoking habit.